Google Scholar
Google Scholar is the scientific counterpart of Google. You can search for books, (peer reviewed) articles, reports, conference papers, and so on. You can narrow down your list of results by selecting a time period and/or language in the left-hand column.
Note that Google Scholar does not check the quality of the sources; they only list them.
How to find sources in Google Scholar
If the full text is available, Google Scholar will search it. If not, it will search abstracts and bibliographical information. Google Scholar uses the same search operators as Google, with a character limit of 256 signs.
- If you use a browser within the UGentNet, you can access the sources UGent has access to. You are browsing within the UGentNet if you use a UGent-computer or if you opened a browser in Athena.
- If you are not browsing within the UGentNet you should be able to see the Ghent University library in your settings. If not, go to menu button (top left) > Settings > Library links to add “University Library Ghent – Fulltext@UGent” and “UNIVERSITEIT GENT (Ghent) – Proquest Fulltext”.

How to optimise your search query
- Use quotation marks to keep phrases together, i.e. “plant diseases”
- Use the AND operator by typing AND or leaving a space, e.g. cattle AND housing
- Use the OR operator by typing OR or |, e.g. beetles | coleoptera
- Use the NOT operator by typing a minus sign (–) immediately followed by the term, e.g.: “forest ecology” –tropics
- Use descriptors like ‘author:’, ‘intitle:’, … immediately followed by the term/name, e.g. author:Todaro
- Use initials for the auhtor’s first name(s)
- Use + immediately followed by the word if it is a word that is easily left out, f.i. articles or prepositions, e.g. +the lancet
- You cannot truncate in Google Scholar
For an advanced search, click the menu button (top left) > Advanced search.
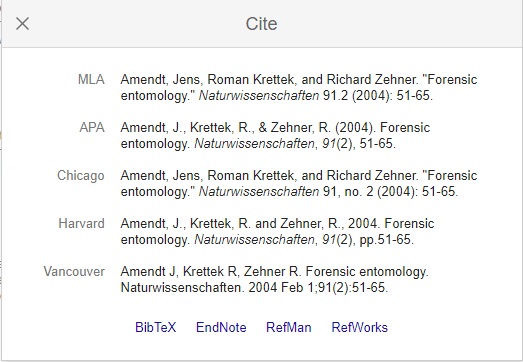
How to find citations in Google scholar
You can also use Google Scholar to format citations in MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard or Vancouver. You can do this by looking up the source and clicking the quotation mark.

How to save search results
Using a Google account, you can compile your own library with references and/or links to the full text. You can do this by clicking the star under the search result. (Make sure that you are logged in with your Google account.)

If your work can be found with Google Scholar, you can make a user profile. This way you can link your own articles and get notifications if someone cites you.
Video
Source reference
More tips
- Google: search tips (Search / find)
- Journal: how to find a print or e-journal or newspaper (Search / find)
- Resources: helpful tools to find literature (Search / find)
- Resources: search and find information (Search / find)
Translated tip
Last modified Nov. 17, 2023, 11:31 a.m.